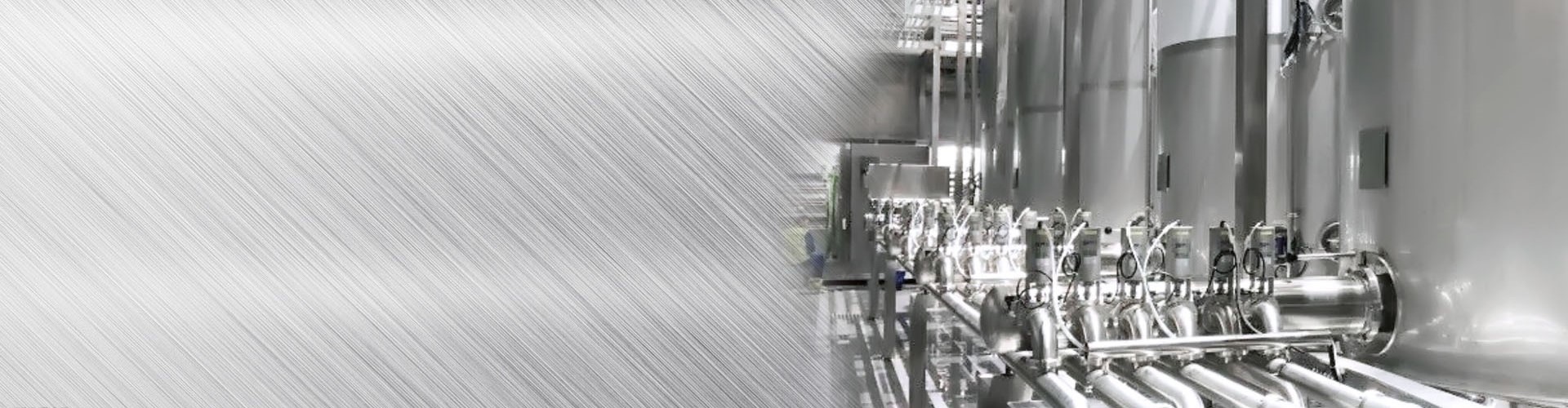

Starting your own milk production plant is a comprehensive venture that involves careful planning, substantial investment, and adherence to strict regulatory standards.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how you could approach this:
2. Business Plan Development: Draft a detailed business plan outlining your vision, objectives, marketing strategies, operational plans, financial forecasts, and risk management strategies.
The cost of setting up a milk production plant can vary widely depending on several factors such as the scale of production, automation level, equipment quality, and whether you're purchasing new or used machinery. To provide a rough estimate:
a. Equipment Costs: A small-scale mini dairy plant could start from around $10,000 to $50,000 for basic equipment like pasteurizers, chillers, storage tanks, and packaging machines. For a medium-sized operation with more advanced technology, the cost could range from $100,000 to $1 million. Large-scale plants with high automation can run into tens of millions.
b. Infrastructure: Renovating or constructing a suitable facility can add significantly to the initial outlay, which could be anywhere from $5,000 to hundreds of thousands, depending on the existing state of the site and required modifications.
c. Operating Costs: Don't forget to budget for ongoing expenses like raw milk purchase, utilities (water, electricity), labor, maintenance, quality control, and marketing. These can amount to a substantial portion of your overall expenses.
d. Permits and Licenses: Legal and regulatory compliance costs can also accumulate, including obtaining licenses, permits, and certifications. While these may not be as substantial as other costs, they are necessary expenditures.
3. Legal & Regulatory Compliance: Register your business and obtain all necessary permits and licenses from local health departments, agricultural authorities, and any other relevant bodies. Familiarize yourself with food safety regulations, environmental laws, and industry standards.
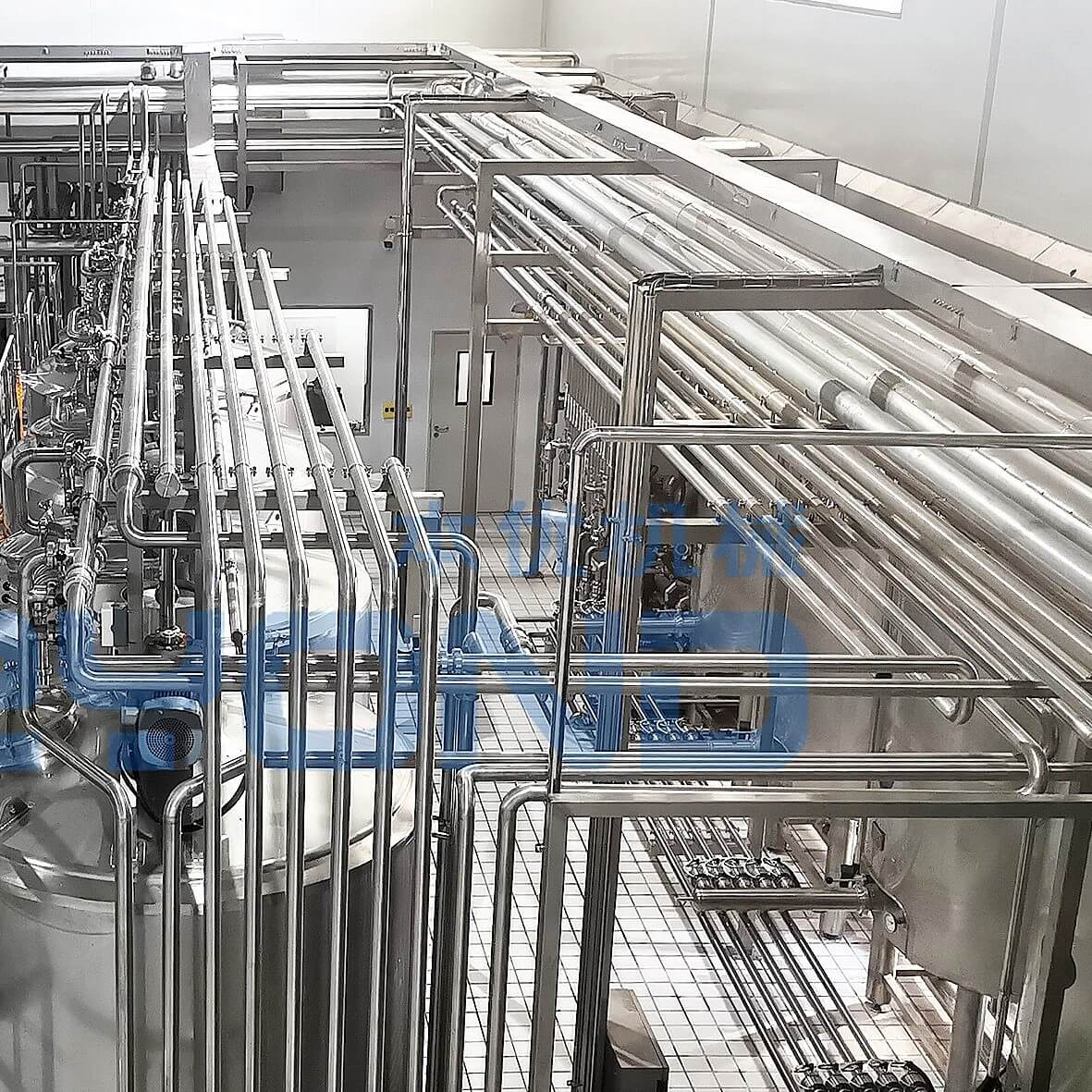
The basic working principle of a Milk Production Plant involves several core steps, from raw milk reception, pretreatment, standardization, sterilization, filling to packaging. Here is a brief explanation of its main process:
a. Raw milk receiving and storage: Fresh milk is collected from the pasture and transported to the factory by refrigerated transport vehicles. At the receiving station, milk will undergo quality testing, including fat content, protein content, microbiological indicators, etc. Qualified milk will be pumped into milk storage tanks for temporary storage.
b. Pretreatment: milk is extracted from milk storage tank, filtered to remove impurities such as hair, dust, etc., and then degassed to remove oxygen in milk, prevent oxidation and deterioration, and reduce the generation of foam. Next, the milk will be heated to a certain temperature for the first sterilization (usually low-temperature pasteurization), killing some bacteria while retaining the original flavor and nutritional content of the milk.
c. Standardization: This step is to adjust the fat content in milk to meet specific product specifications (such as full fat, low-fat, skim milk). By using centrifugal separation technology, milk is divided into two parts: fat rich cream layer and skim milk, and then re mixed according to the required ratio.
d. Homogenization: In order to prevent fat from floating up and forming a milk fat layer, milk is subjected to high-pressure homogenization treatment, which breaks down large fat globules into small particles, evenly distributing fat in the milk and improving the stability and taste of the product.
e. High temperature sterilization/ultra-high temperature sterilization (HTST/UHT): According to product requirements, milk will be further subjected to high temperature short-term sterilization (HTST) or ultra-high temperature sterilization (UHT). HTST is typically used for pasteurized milk with a shorter shelf life, while UHT is used to produce milk that can be stored at room temperature, thoroughly sterilized at extremely high temperatures in a short period of time, and quickly cooled and sealed to extend the shelf life.
f. Filling and sealing: Milk that has been sterilized enters a sterile filling machine and is filled into pre disinfected packaging containers such as plastic bottles, paper boxes, or glass bottles in a sterile environment. The containers are immediately sealed and sealed to maintain sterility.
g. Packaging and Inspection: The filled milk undergoes automatic inspection to ensure that each package is sealed properly and meets hygiene standards, and then undergoes packaging, labeling, coding, and other operations to prepare for delivery.
5. Equipment Sourcing: Based on your production scale and product range, identify and purchase or lease the necessary equipment, including milk reception systems, pre-treatment units, pasteurizers, homogenizers, filling machines, packaging equipment, and a CIP system.
a. Raw milk receiving and storage system: including milk tanker receiving station, raw milk storage tank, refrigeration equipment, etc., to ensure that milk is stored at a suitable temperature and kept fresh.
b. Preprocessing equipment: • Filter: used to remove impurities from milk, such as fragments, hair, etc Degassing device: removes oxygen from milk through vacuum or physical methods.
c. Standardized equipment: Separators and mixing equipment used to adjust the fat content in milk to meet different product specifications.
d. Homogenizer: Refining the fat globules in milk through high pressure to improve product stability and taste.
e. Sterilization equipment: • Pasteurization machine (HTST): used for low-temperature and long-term sterilization to maintain the original flavor of milk Ultra high temperature sterilizer (UHT): Instantaneous high-temperature sterilization enables products to be stored at room temperature for a long time.
f. Filling and capping system: Aseptic filling machine and capping machine ensure rapid filling and sealing of milk under sterile conditions.
g. Packaging equipment: including automatic labeling machines, inkjet printers, wrapping machines, etc., to complete the outer packaging of products.
h. Cleaning and Disinfection Equipment (CIP System): Used for cleaning and disinfecting various containers and pipelines on the production line to ensure the hygiene and safety of the production environment.
i. Automation control system: including PLC programming logic controller, SCADA monitoring system, etc., to achieve automation control and monitoring of the production process.
j. Testing and laboratory equipment: such as mass spectrometers, biochemical analyzers, etc., used for quality testing of raw materials and finished products to ensure food safety. These devices together form a complete milk processing chain, from raw material reception to finished product packaging, every step is crucial.
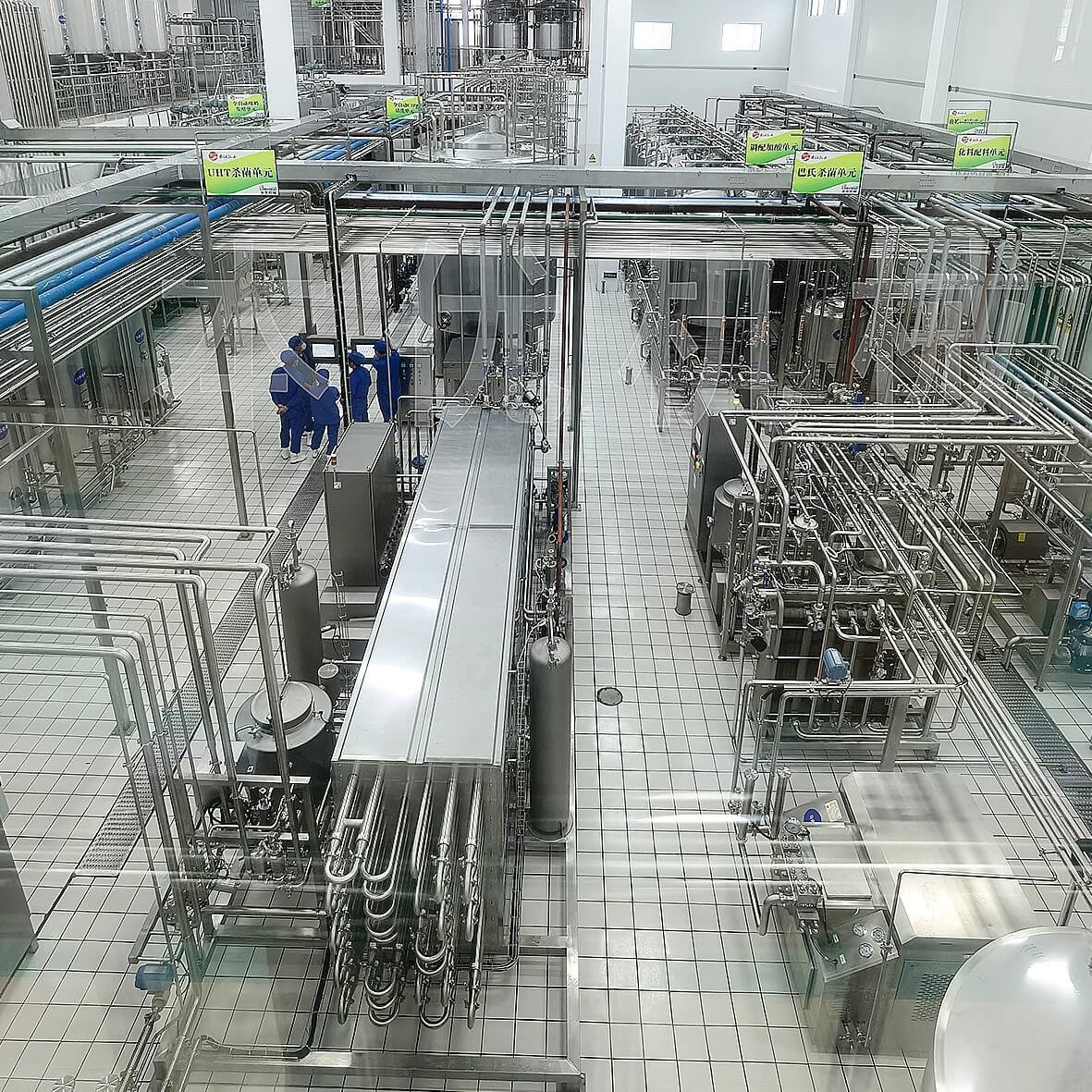

6. Supply Chain Setup: Establish relationships with dairy farmers or suppliers to ensure a consistent and high-quality milk supply. Plan for storage facilities and cold chain logistics.
7. Staffing & Training: Hire a skilled workforce, including production managers, quality control personnel, machine operators, and administrative staff. Provide them with comprehensive training on hygiene practices, equipment operation, and safety protocols.
8. Quality Control & Testing: Set up an in-house laboratory or partner with certified labs to perform regular quality checks on incoming milk and finished products, adhering to food safety standards.
9. Marketing & Sales Strategy: Develop a robust marketing plan to create brand awareness, build relationships with distributors, retailers, and potentially directly with consumers. Explore online sales channels as well.
10. Launch & Continuous Improvement: Once operations begin, gather customer feedback, monitor performance metrics, and continuously improve processes and products to stay competitive.This is a high-level overview, and each step involves many sub-steps and considerations. It's advisable to consult with industry experts, financial advisors, and legal professionals throughout the process.
Shanghai Beyond Machinery Co., Ltd.
Beyond Machinery specializes in the design and manufacturing of milk production plant.Please contact us now, and ourprofessional technical engineers will customize the equipment plan for milk production plant and provide a quotation.Please contact us now to obtain the latest equipment plan and quotation.



